Internal AI Content Tool
Role: Project Lead, Content Designer
Industry: Travel
Duration: 6 months
Challenge
UX audits consistently showed low content alignment across the product. Designers and PMs struggled to apply content guidelines and often relied on consumer AI tools that produced low quality content.
At the same time, the Content Design team was overloaded with ad-hoc requests.
Goals
Enable Product Designers, Product Managers, and Engineers to self-serve ad-hoc content needs.
Improve the quality and consistency of product communication by embedding guidelines and tone of voice into the tool.
Free up content design team capacity to focus on strategic, end-to-end work.
Process
1. Diagnosed the problem
Used heuristic analysis and UX audits to identify where and how misalignment started.
Used historical Writer.AI requests to design the tool around real usage patterns.
Found that most requests were repetitive, lacked context (and understanding of our guidelines).
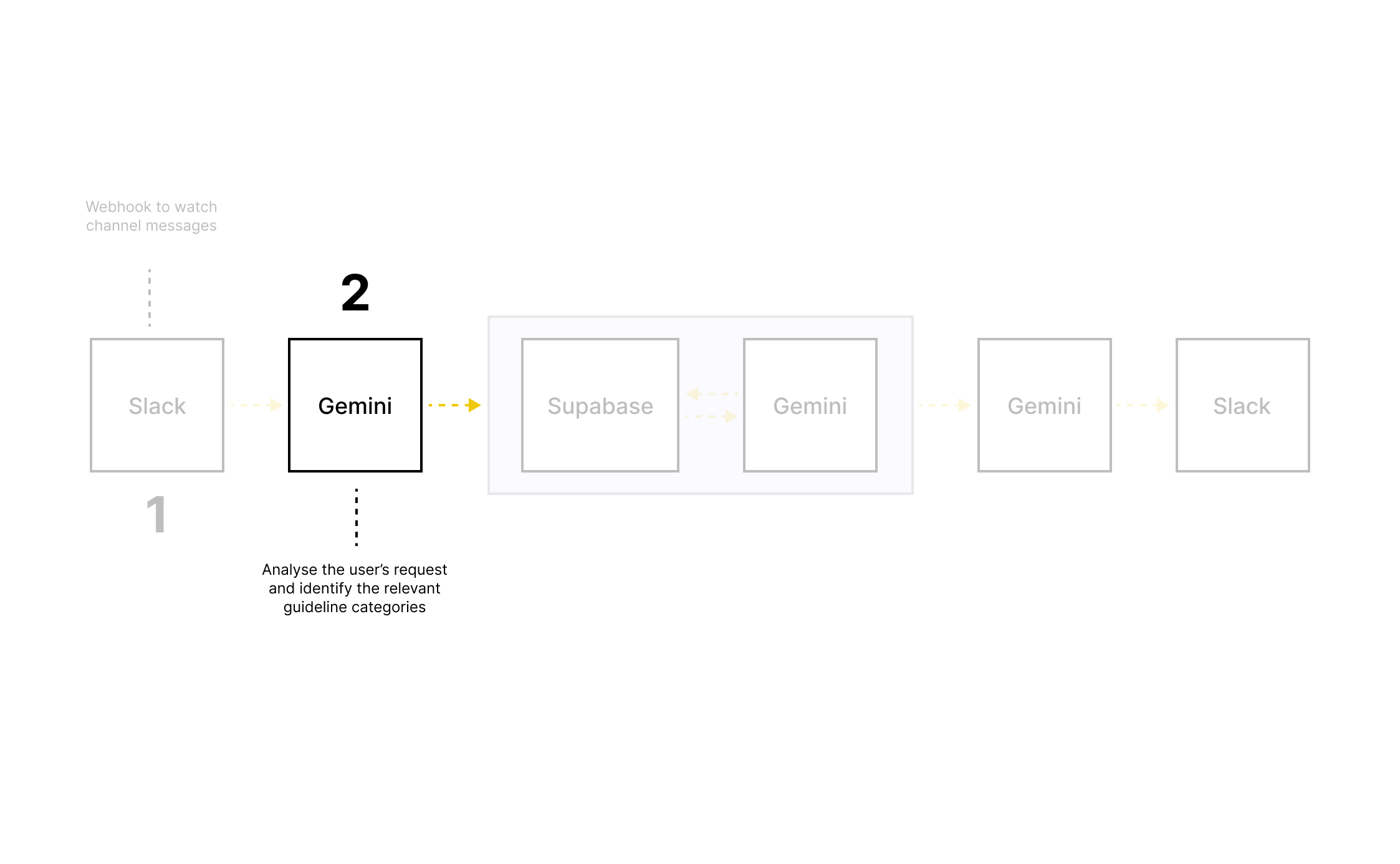
2. Defined clear boundaries for AI
Explicitly defined what the tool should do:
Apply content principles and terminology
Produce content based on guidelines and our product’s context
Also defined what it should not do:
Invent rules
Play with creativity over clarity
Act as a source of truth
This framing helped prevent AI overreach early on.
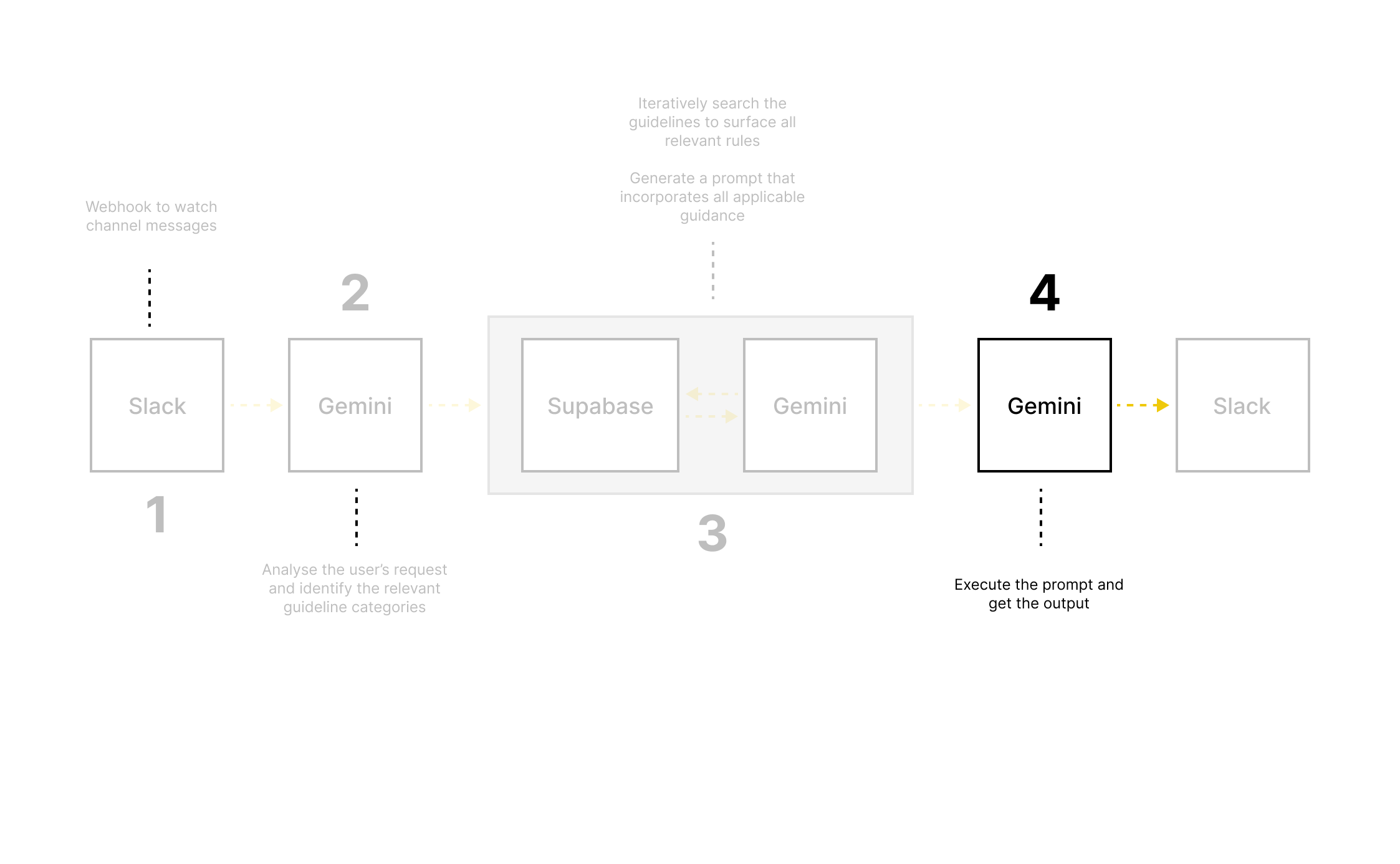
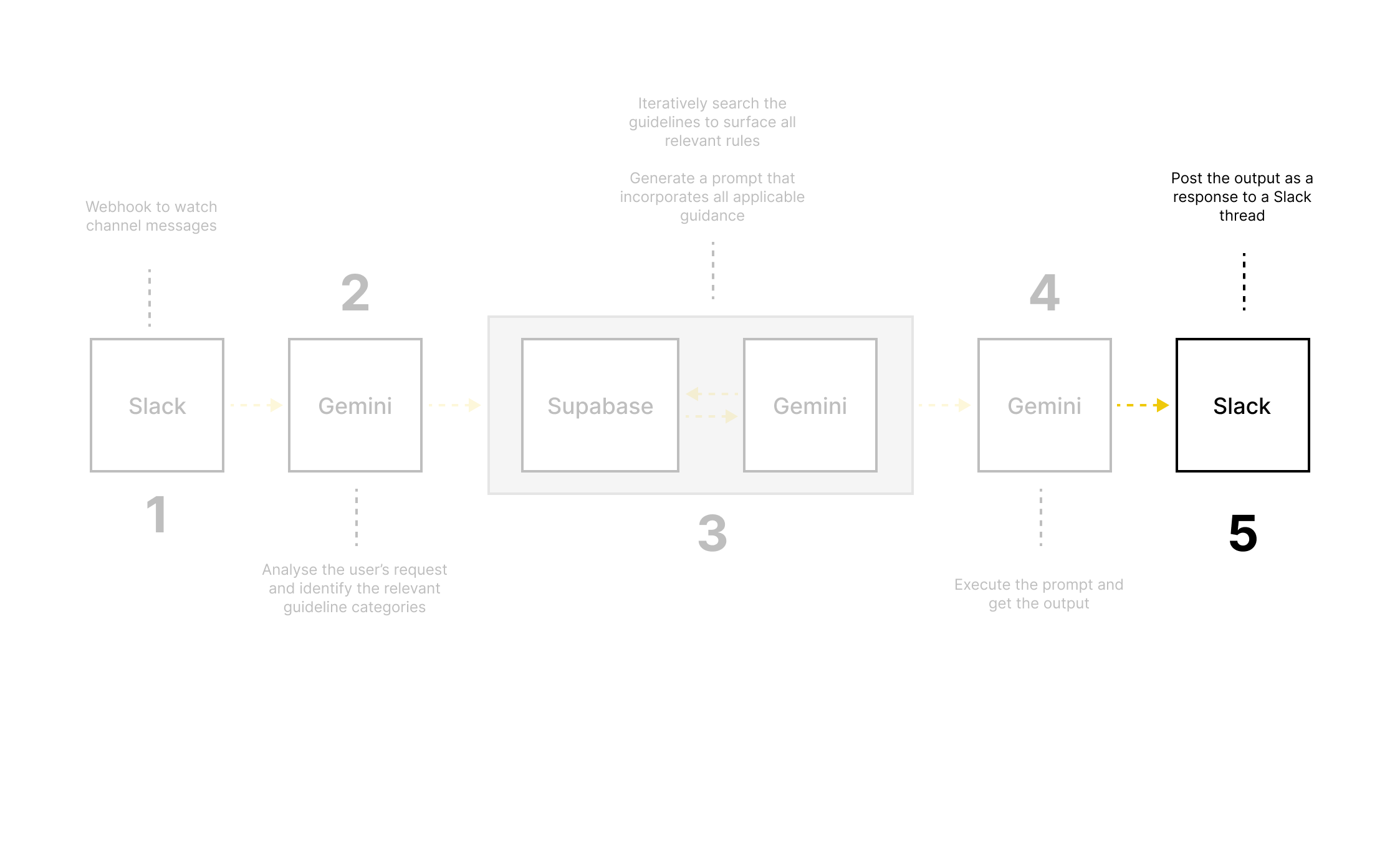
3. Prototyped the tool
Ran an internal AI hackathon to validate feasibility.
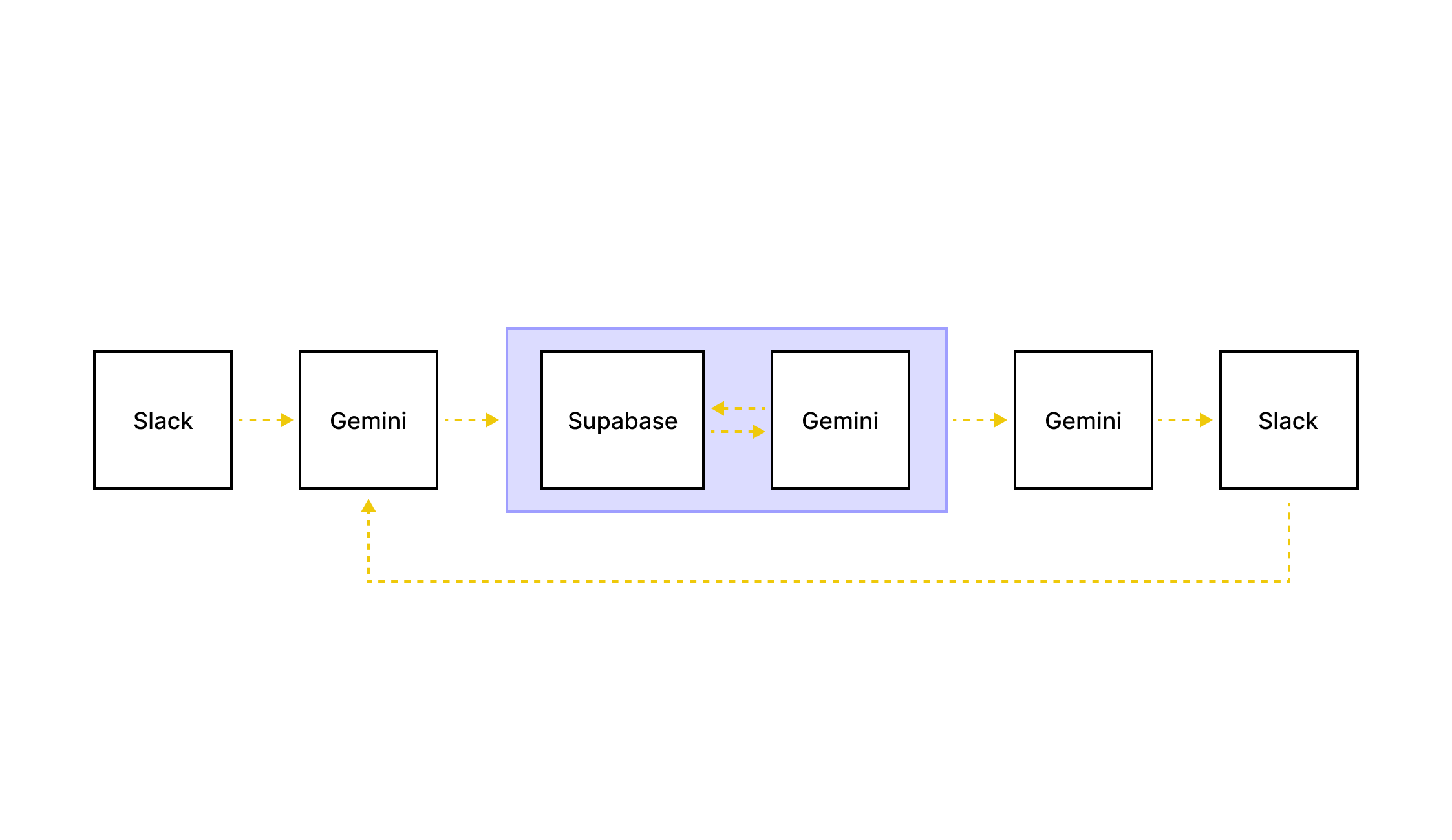
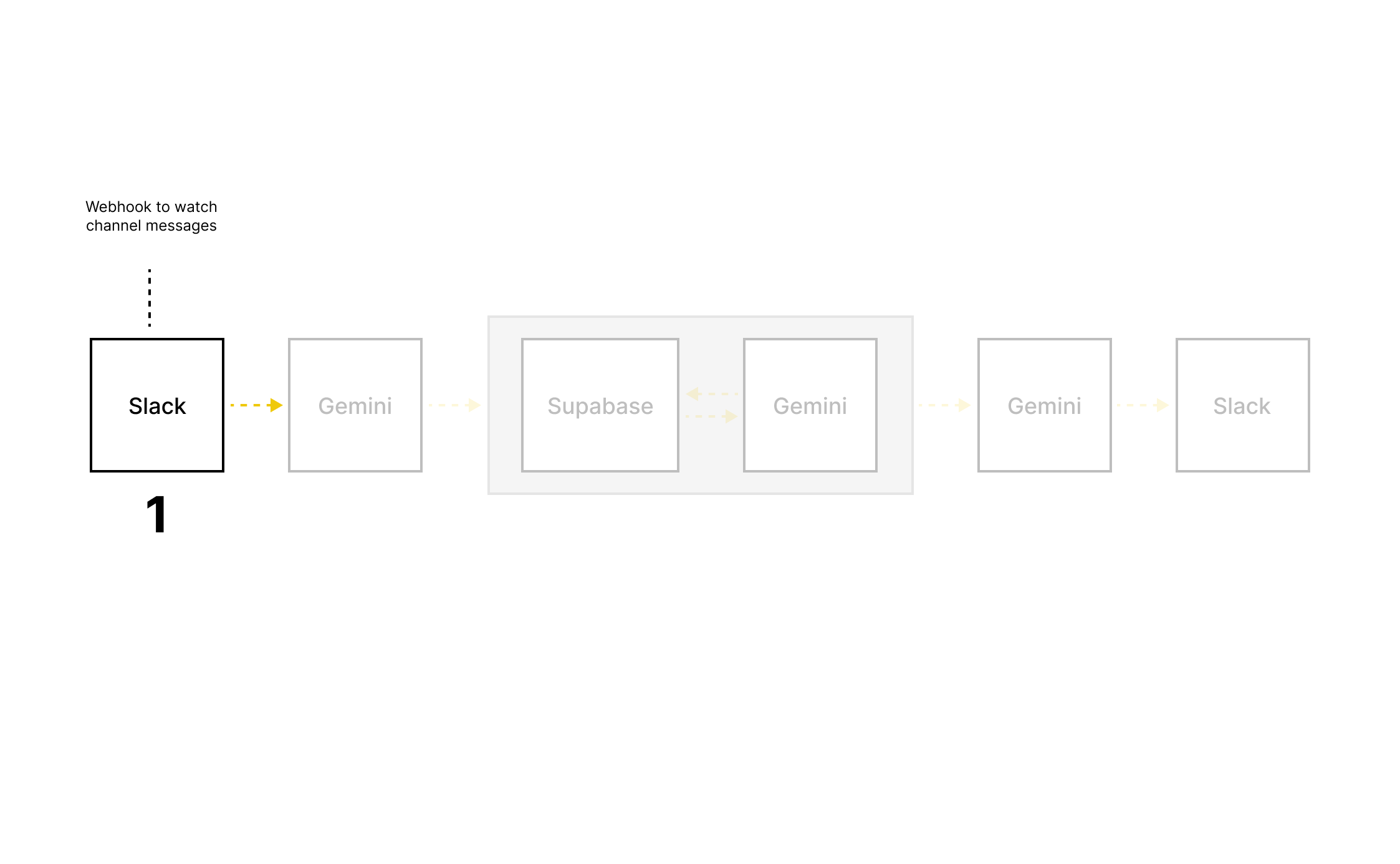
Built an early prototype using:
Slack for access and adoption
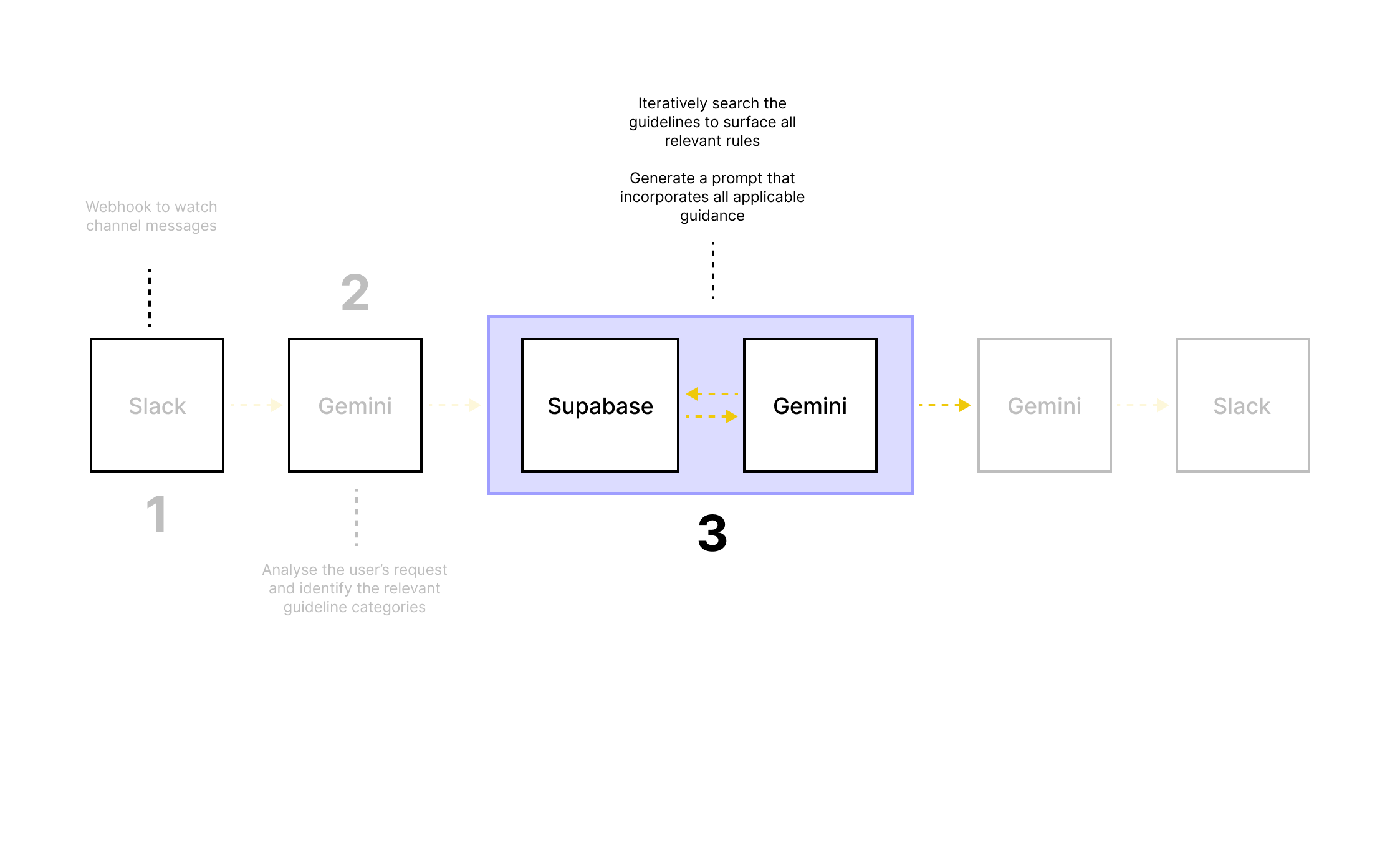
Supabase to store and fetch content guidelines
Make for automation
OpenAI for generation
Designed prompt logic based on real request patterns.
Benchmarked outputs against Writer.AI to understand trade-offs.
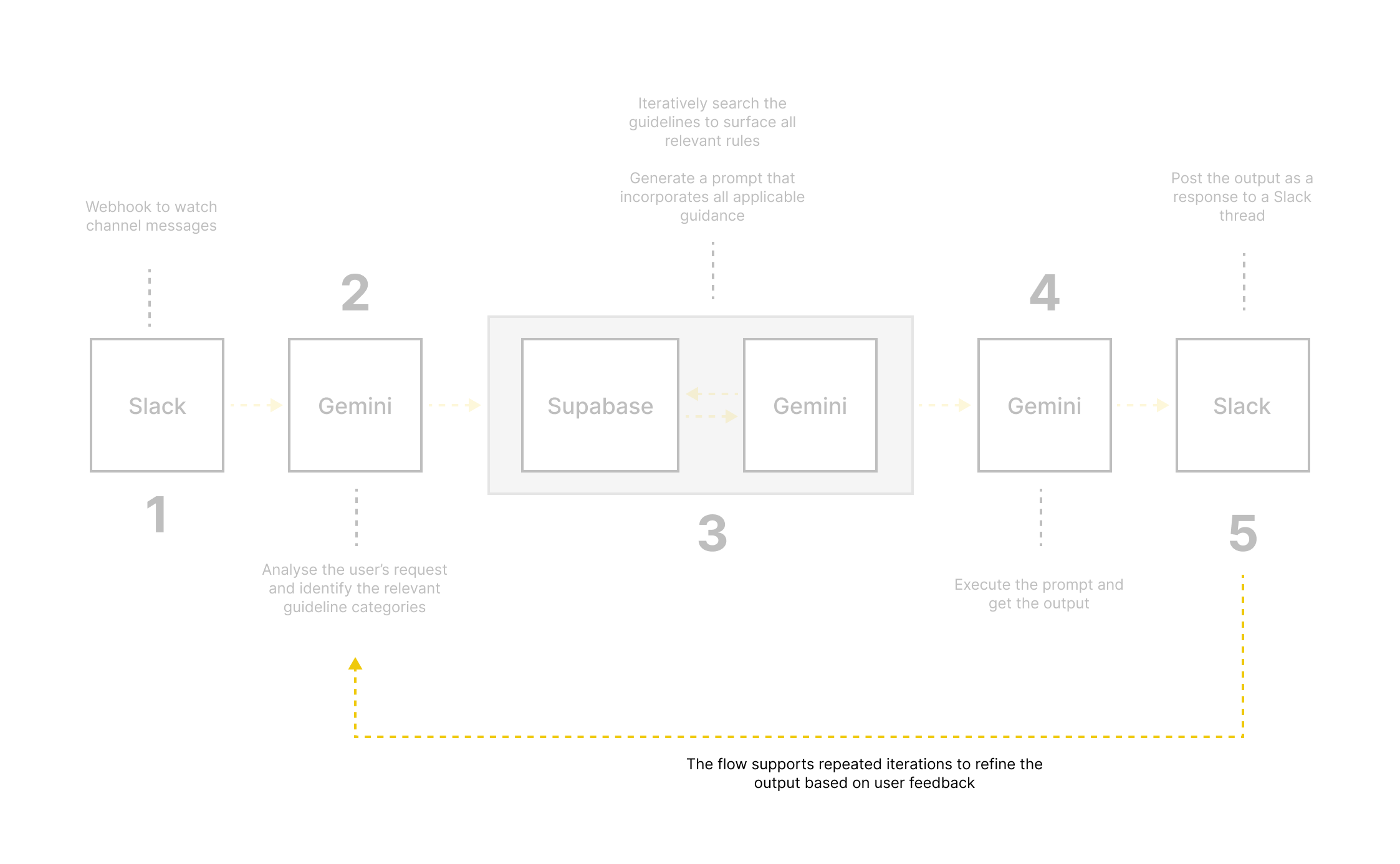
4. Iterated based on the flow failures
Tested multiple prompt structures and rule application models.
Early failure: applying only 1–2 guidelines led to inconsistent or misleading outputs.
Iterated toward multi-rule application with clearer prioritisation and constraints.
5. Validated with the teams
Recruited beta users across product, design, and engineering.
Prepared lightweight onboarding focused on when to use the tool (and when not to).
Collected qualitative feedback and usage patterns.
Refined prompts, guardrails, and guidance based on real-world use.
6. Launched and defined the governance model
Rolled out the tool company-wide.
Defined a regular audit cadence to:
Review output quality
Track content alignment improvements
Update guidelines and prompts over time
Solution
Results
Improved content alignment across product.
Reduced reliance on expensive third-party AI tools (saving money for the company).
Fewer ad-hoc content questions and Office Hours meetings.
More time for content designers to focus on strategic work.